Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness, is a refractive error, which causes the eye to stop refracting light properly. This prevents someone from seeing images clearly. In the case of hyperopia, light focuses behind the retina instead of on the retina.
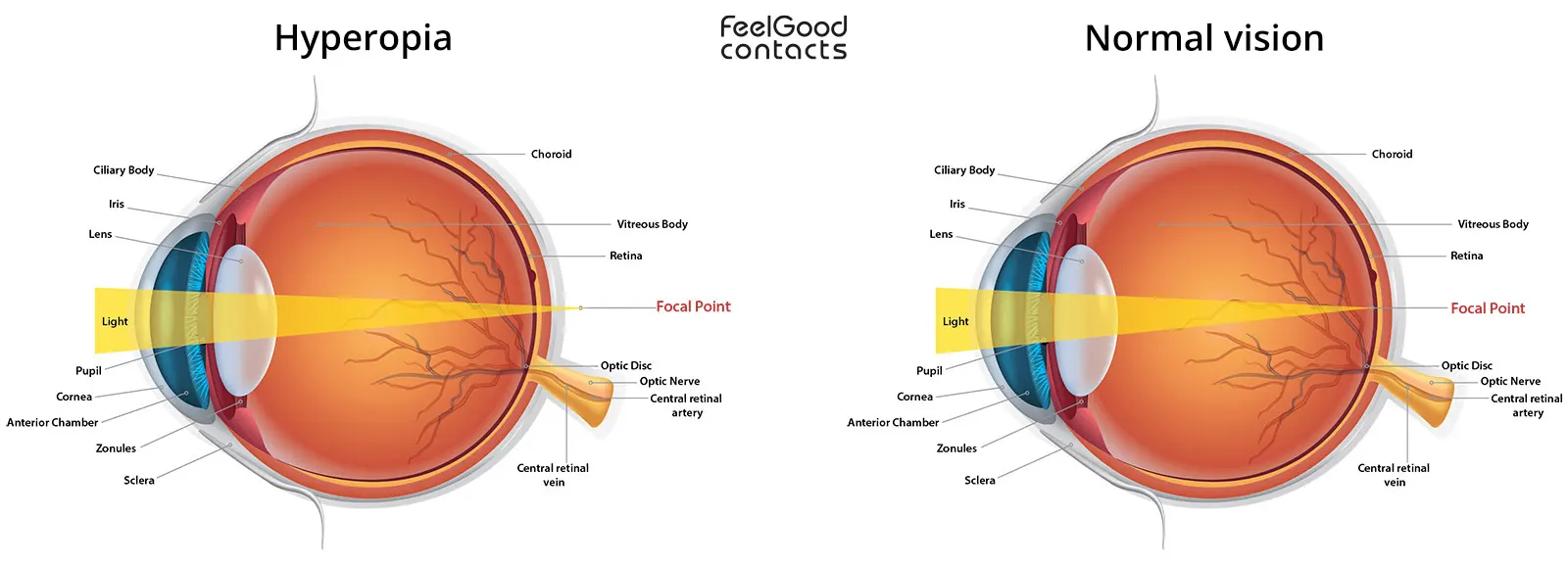
Hyperopia is a common vision problem. It mostly occurs when a person’s eyeball is too short, or the cornea is too flat. Because of this, the eye fails to focus light correctly on the retina.
Symptoms of farsightedness

Signs and symptoms of farsightedness include:
- Squinting to see clearly
- Eye strain
- Regular headaches after focusing on nearby objects
- Trouble seeing objects close up
What causes hyperopia?
A refractive error causes hyperopia. A refractive error happens when your cornea isn't smoothly curved. As a result, light rays stop refracting properly, causing a vision problem.
Hyperopia happens when light focus behind the retina due to your eyeball being too short . This results in blurry vision of near objects.
There is no exact cause of hyperopia; however, hyperopia can be inherited if you have a first-degree relative such as siblings or parents with the condition.
How does hyperopia affect vision?
Hyperopia affects vision by causing close up objects to appear blurry, while distant objects will appear relatively in focus. The condition can affect people of all ages, including babies and children.
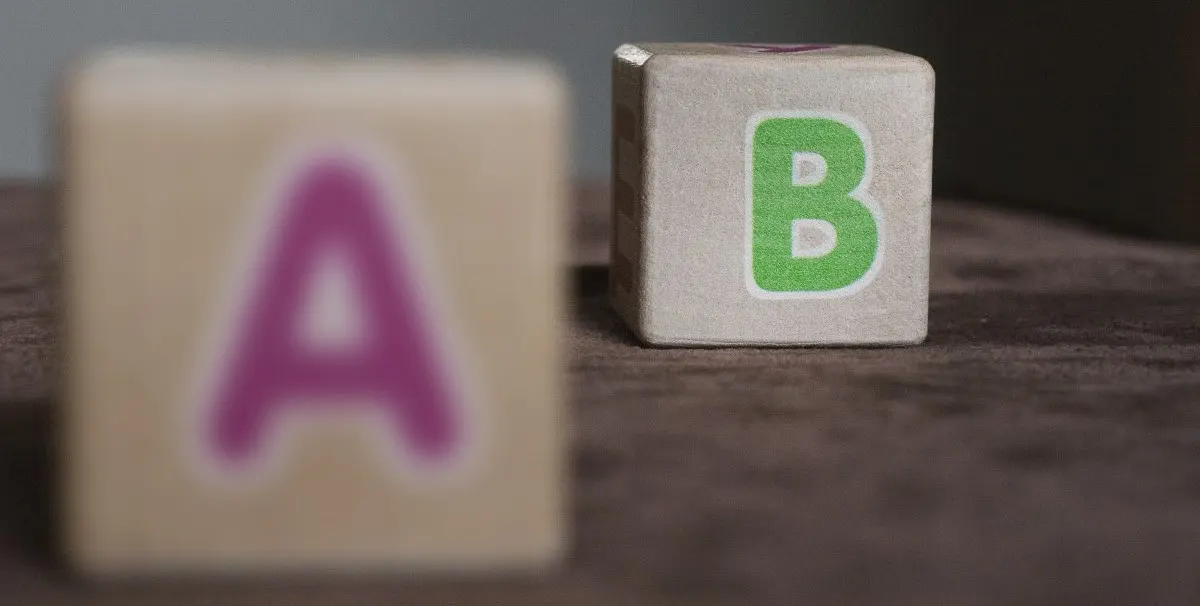

Complications:
Complications of hyperopia are more common in children than adults. Children with extreme hyperopia may over focus and experience double vision as a result. Double vision can then cause the following problems:
- Crossed eyes (strabismus) - young children with hyperopia are at a higher risk of developing crossed eyes; however, glasses can correct this.
- Lazy eyes (amblyopia) - this is the result of one eye becoming more reliable and more dominant than the other.
Other complications of hyperopia include learning problems and delays in development.
When to see a doctor
You should see a doctor if your degree of hyperopia hinders your ability to perform tasks to your maximum potential.
Many very young children have mild hypermetropia that gets better by itself as they grow older.
It may not be evident to you if you're having problems with your vision. For this reason, comprehensive eye tests are recommended once every two years.
Diagnosis of hyperopia
A standard eye exam which includes various vision tests such as a refraction assessment and an eye health check, is used to diagnose hyperopia.
Refraction assessments can also determine other visual impairments such as near-sightedness myopia, astigmatism and presbyopia.
Your optician may ask you to look through various lenses to check your vision. They may also dilate your pupils with eye drops.
If you're long-sighted, you'll be given a prescription by your optometrist for the correction your eyes need.
How is hyperopia treated?
Fortunately, you can treat hyperopia with corrective lenses such as eyeglasses or contact lenses. Wearing glasses or contact lenses can counteract the lack of curvature to your cornea to treat farsightedness.
Laser eye surgery is also an alternative way to treat hyperopia, as well as other refractive errors.
What type of lens corrects hyperopia?
Aspheric high index lenses are used to correct hyperopia. Depending on how strong the prescription is, spherical lenses can also be used to correct hyperopia. Aspheric high index lenses are especially great for higher prescriptions and are thinner and lighter with a slimmer and more attractive profile.
High index lenses reflect more light than standard plastic lenses. So, if you require glasses, make sure you get an anti-reflective coating to get rid of any reflections.
Spherical contact lenses can also correct hyperopia. Before choosing contact lenses, make sure to consider your wearing options. For example, whether you'd like daily disposables, two weekly or monthly contact lenses.
Glasses and contact lens prescriptions for farsightedness usually begin with plus numbers.
Can hyperopia be cured?
Refractive surgery cures hyperopia, both mild to moderate, by reshaping the curvature of your cornea. While laser surgery is a popular choice for patients with hyperopia, it may not be suitable for everyone.
What is the difference between presbyopia and hyperopia?
Presbyopia is an age-related eye condition which usually occurs in people over the age of 40. Hyperopia differs as it can occur during childhood or at birth.
Hyperopia is caused when the cornea is flat, whereas presbyopia is caused by a hardening of the lens over time.
For a better understanding of refractive errors including hyperopia, presbyopia, astigmatism and myopia, visit our vision simulator.
Quick links:
Do I need an eye test?
How long is a contact lens prescription good for?
A guide to myopia
Disclaimer: The advice in this article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical care or an in-person check-up. Please check with an eyecare professional before purchasing any products or remedies. For information on our article review process, please refer to our Editorial Policy.

 Offers
Offers Account
Account
 Favorite
Favorite
 Basket
Basket

 OFFERS
OFFERS